
Subject: Class 11 Physics Online Coaching For Neet Exam
Phone: +91-9868233590
Class 11 Physics Online Coaching For Neet Exam
Waves Class 11 Physics Notes
WAVES
WAVE MOTION
Wave motion is a type of motion in which the disturbance travels from one point of the medium to another but the particles of the medium do not travel from one point to another.
For the propagation of wave, medium must have inertia and elasticity. These two properties of medium decide the speed of wave.
There are two types of waves
- Mechanical waves : These waves require material medium for their propagation. For example : sound waves, waves in stretched string etc.
- Non-mechanical waves or electromagnetic waves : These waves do not require any material medium for their propagation. For example : light waves, x-rays etc.
There are two types of mechanical waves
- Transverse waves : In the transverse wave, the particles of medium oscillate in a direction perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. Waves in stretched string, waves on the water surface are transverse in nature.
Transverse wave can travel only in solids and surface of liquids.
Transverse waves propagate in the form of crests and troughs.
All electromagnetic waves are transverse in nature.
- Longitudinal waves : In longitudinal waves particles of medium oscillate about their mean position along the direction of wave propagation.
Sound waves in air are longitudinal. These waves can travel in solids, liquids and gases.
Longitudinal waves propagate through medium with the help of compressions and rarefactions.
EQUATION OF A HARMONIC WAVE
Harmonic waves are generated by sources that execute simple harmonic motion.
A harmonic wave travelling along the positive direction of x-axis is represented by
where,
y = displacement of the particle of the medium at a location x at time t
A = amplitude of the wave
λ = wavelength
T = time period
v = wave velocity in the medium
ω = 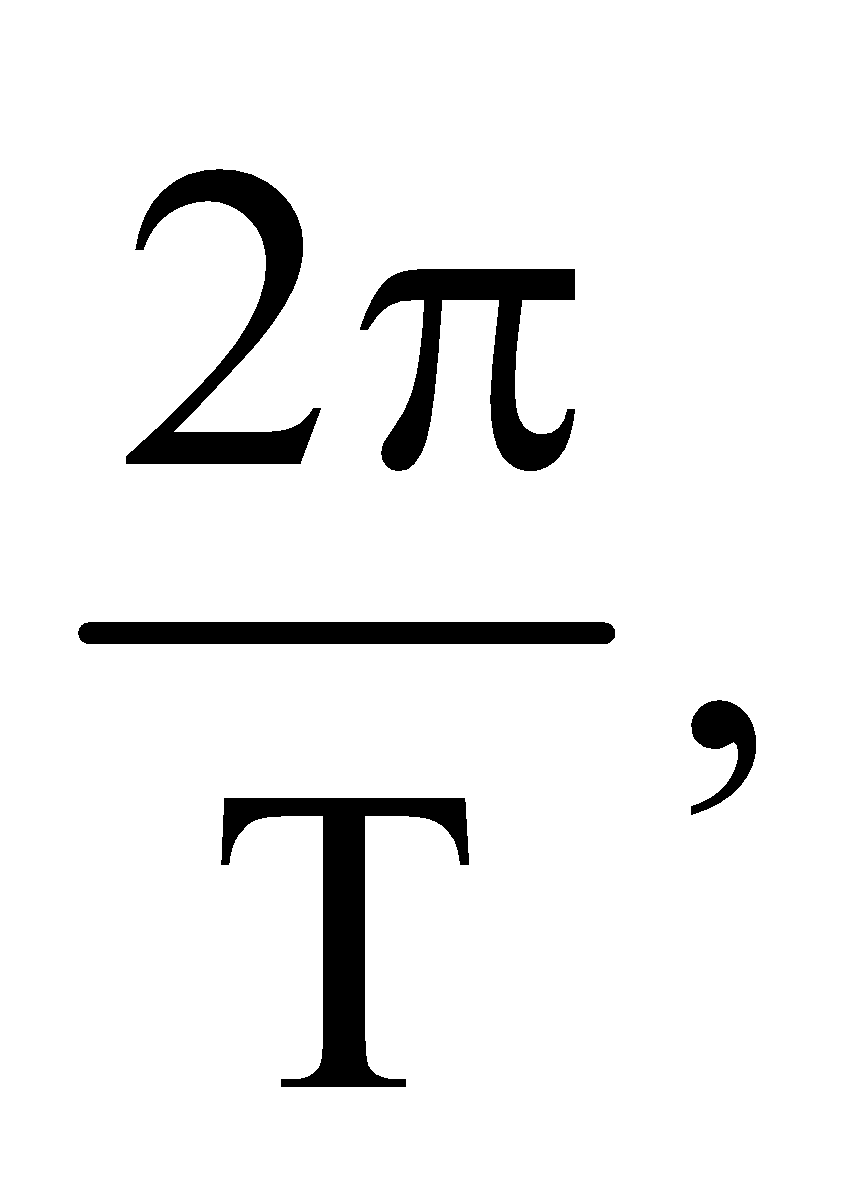 angular frequency
angular frequency
K =  angular wave number or propagation constant.
angular wave number or propagation constant.
If the wave is travelling along the negative direction of x-axis then
DIFFERENTIAL EQUATION OF WAVE MOTION

RELATION BETWEEN WAVE VELOCITY AND PARTICLE VELOCITY
The equation of a plane progressive wave is
The particle velocity
Slope of displacement curve or strain
Dividing eqn. (ii) by (iii), we get
i.e., Particle velocity = – wave velocity × strain.
Particle velocity changes with the time but the wave velocity is constant in a medium.
RELATION BETWEEN PHASE DIFFERENCE, PATH DIFFERENCE AND TIME DIFFERENCE
- Phase difference of 2π radian is equivalent to a path difference λ and a time difference of period T.
- Phase difference =
× path difference
- Phase difference =
× time difference
- Time difference =
× path difference
SPEED OF TRANSVERSE WAVES
- The speed of transverse waves in solid is given by
where η is the modulus of rigidity of the solid and ρ is the density of material.
- The speed of transverse waves on stretched string is given by
where T is the tension in the string and μ is the mass per unit length of the string.
SPEED OF LONGITUDINAL WAVES
The speed of longitudinal waves in a medium of elasticity E and density ρ is given by 
For solids, E is replaced by Young's modulus (Y)

For liquids and gases, E is replaced by bulk modulus of elasticity (B)
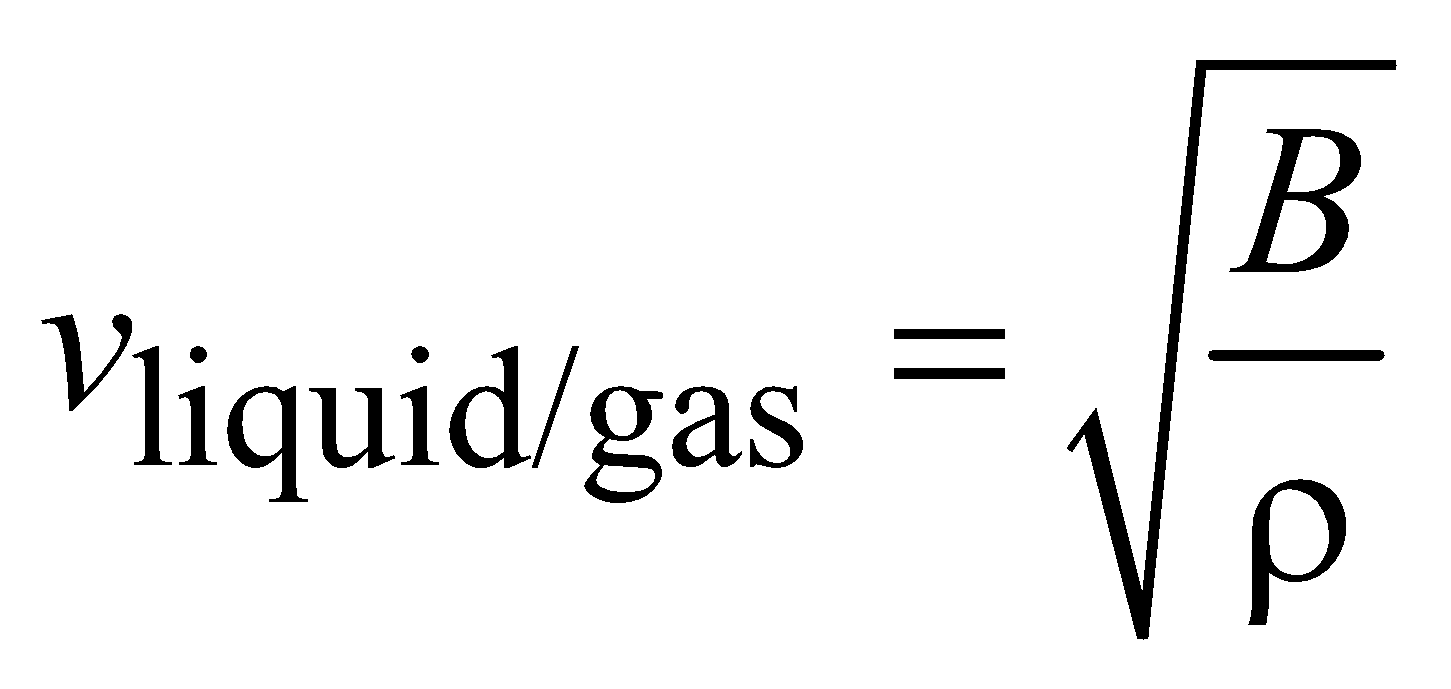
The density of a solid is much larger than that of a gas but the elasticity is larger by a greater factor.
vsolid > vliquid > vgas
SPEED OF SOUND IN A GAS
NEWTON'S FORMULA
where P is the atmospheric pressure and ρ is the density of air at STP.
LAPLACE'S CORRECTION
where γ is the ratio of two specific heats Cp and Cv
POWER AND INTENSITY OF WAVE MOTION
If a wave is travelling in a stretched string, energy is transmitted along the string.
Power of the wave is given by
Intensity is flow of energy per unit area of cross section of the string per unit time.
PRINCIPLE OF SUPERPOSITION OF WAVES
If two or more waves arrive at a point simultaneously then the net displacement at that point is the algebraic sum of the displacement due to individual waves.
y = y1 + y2 + ............... + yn.
where y1, y2 .......... yn are the displacement due to individual waves and y is the resultant displacement.
INTERFERENCE OF WAVES
When two waves of equal frequency and nearly equal amplitude travelling in same direction having same state of polarisation in medium superimpose, then intensity is different at different points. At some points intensity is large, whereas at other points it is nearly zero.
Consider two waves
y1 = A1sin (ωt – kx) and y2 = A2 sin (ωt – kx + φ)
By principle of superposition
y = y1 + y2 = A sin (ωt – kx + δ)
where, A2 = A12 + A22 + 2A1A2 cos φ,
and 
As intensity I ∝ A2
So, resultant intensity I = I1 + I2 + 
For constructive interference (maximum intensity) :
Phase difference, φ = 2nπ and path difference = nλ where n = 0, 1, 2, 3, ...
⇒ Amax = A1 + A2 and Imax = I1 + I2 + 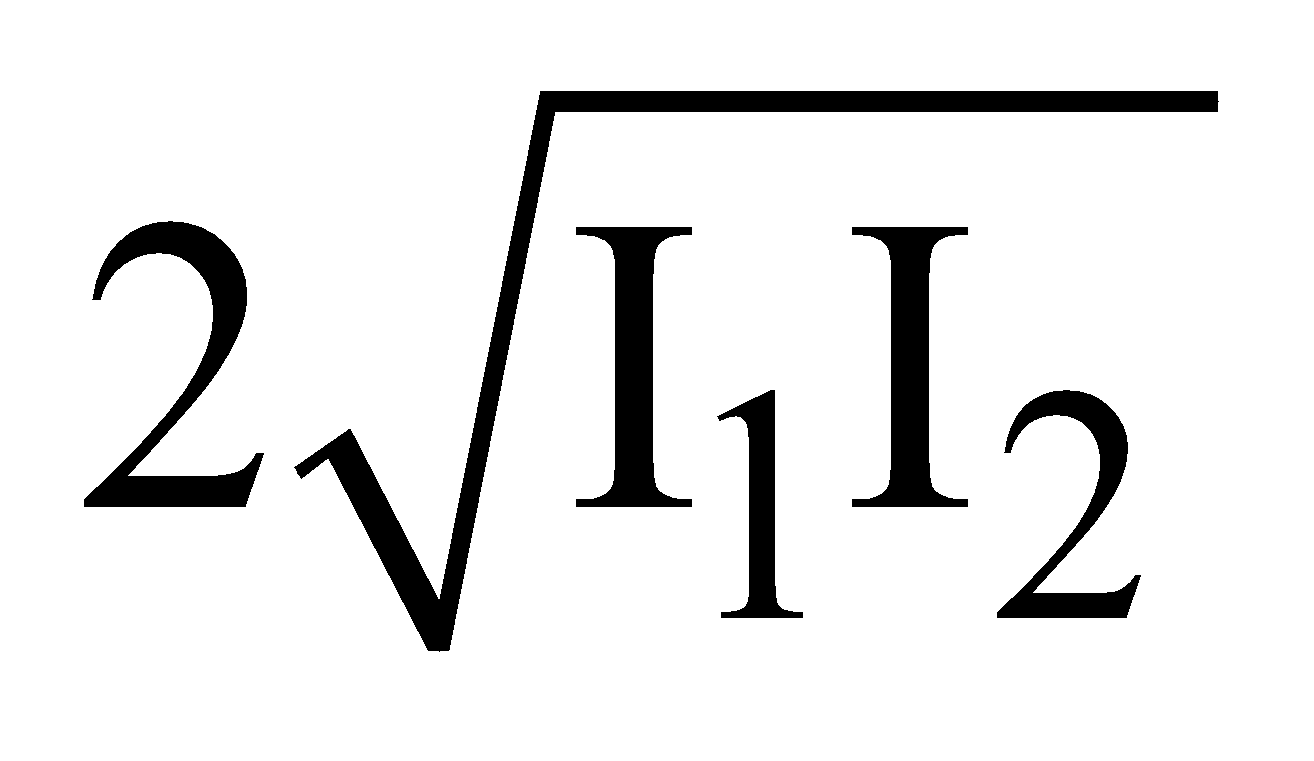

For destructive interference (minimum intensity) :
Phase difference, φ = (2n + 1)π,
and path difference =  ; where n = 0, 1, 2, 3, ...
; where n = 0, 1, 2, 3, ...
⇒ Amin = A1 – A2 and Imin = I1 + I2 – 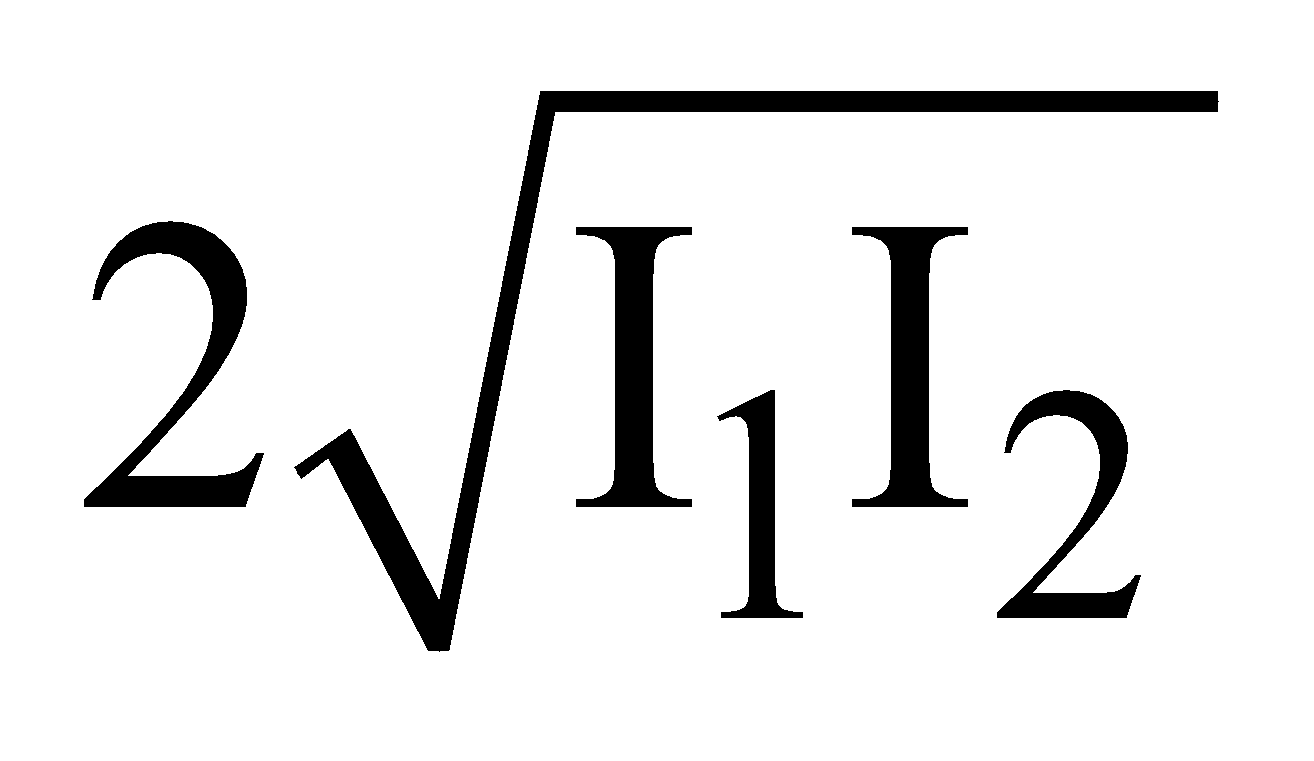

RESULTS
- The ratio of maximum and minimum intensities in any interference wave form.
- Average intensity of interference in wave form :
Put the value of Imax and Imin
or Iav = I1 + I2
If A = A1 = A2 and I1 = I2 = I
then Imax = 4I, Imin = 0 and Iav = 2I
- Condition of maximum contrast in interference wave form
A1 = A2 and I1 = I2
then Imax = 4I and Imin = 0
For perfect destructive interference we have a maximum contrast in interference wave form.
REFLECTION OF WAVES
A mechanical wave is reflected and refracted at a boundary separating two media according to the usual laws of reflection and refraction.
When sound wave is reflected from a rigid boundary or denser medium, the wave suffers a phase reversal of π but the nature does not change i.e., on reflection the compression is reflected back as compression and rarefaction as rarefaction.
When sound wave is reflected from an open boundary or rarer medium, there is no phase change but the nature of wave is changed i.e., on reflection, the compression is reflected back as rarefaction and rarefaction as compression.
KEEP IN MEMORY
- For a wave, v = f λ
- The wave velocity of sound in air
- Particle velocity is given by
. It changes with time. The wave velocity is the velocity with which disturbances travel in the medium and is given by
.
- When a wave reflects from denser medium the phase change is π and when the wave reflects from rarer medium, the phase change is zero.
- In a tuning fork, the waves produced in the prongs is transverse whereas in the stem is longitudinal.
- A medium in which the speed of wave is independent of the frequency of the waves is called non-dispersive. For example air is a non-dispersive medium for the sound waves.
- Transverse waves can propagate in medium with shear modulus of elasticity e.g., solid whereas longitudinal waves need bulk modulus of elasticity hence can propagate in all media solid, liquid and gas.
ENERGY TRANSPORTED BY A HARMONIC WAVE ALONG A STRING
Kinetic energy of a small element of length dx is
and potential energy stored

BEATS
When two wave trains slightly differing in frequencies travel along the same straight line in the same direction, then the resultant amplitude is alternately maximum and minimum at a point in the medium. This phenomenon of waxing and waning of sound is called beats.
Let two sound waves of frequencies n1 and n2 are propagating simultaneously and in same direction. Then at x=0
y1 = A sin 2π n1t, and y2 = A sin 2π n2t,
For simplicity we take amplitude of both waves to be same.
By principle of superposition, the resultant displacement at any instant is
y = y1 + 2 = 2A cos 2π nAt sin 2π navt
where 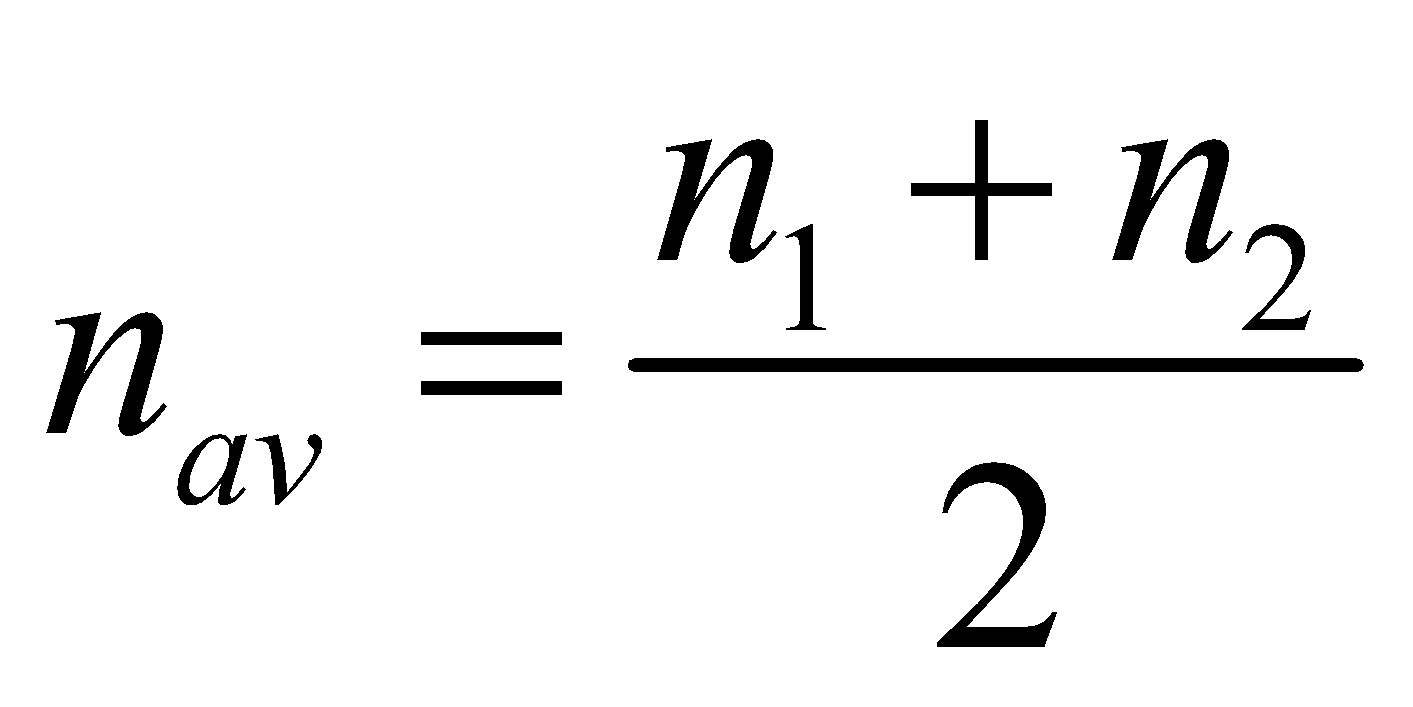 ,
, 
⇒ y = Abeat sin 2π navt ..................(i)
It is clear from the above expression (i) that
- Abeat = 2A cos 2πnAt, amplitude of resultant wave varies periodically as frequency
A is maximum when 
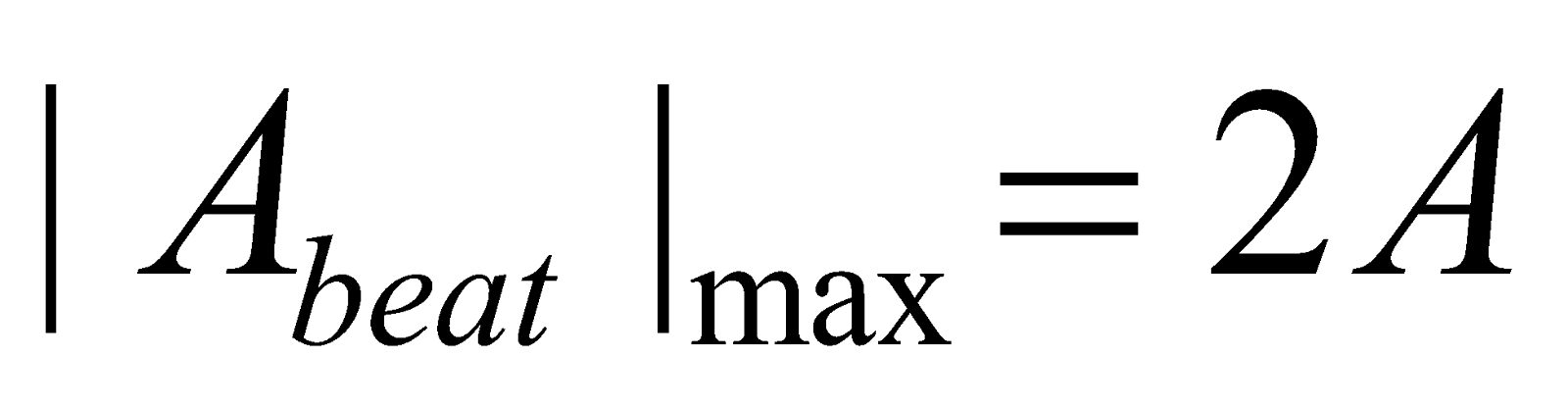
A is minimum when 

- Since intensity is proportional to amplitude i.e.,
For Imax cos 2π nAt = ± 1 For Imin
i.e., 2π nAt = 0,π, 2π 2π nAt = π/2, 3π/2
i.e., t = 0, 1/2nA, 2/2nA t = 1/4nA, 3/4nA.......
So time interval between two consecutive beat is

Number of beats per sec is given by

So beat frequency is equal to the difference of frequency of two interfering waves.
To hear beats, the number of beats per second should not be more than 10. (due to hearing capabilities of human beings)
FILING/LOADING A TUNING FORK
On filing the prongs of tuning fork, raises its frequency and on loading it decreases the frequency.
- When a tuning fork of frequency ν produces Δν beats per second with a standard tuning fork of frequency ν0, then
If the beat frequency decreases or reduces to zero or remains the same on filling the unknown fork, then 
- If the beat frequency decreases or reduces to zero or remains the same on loading the unknown fork with a little wax, then
If the beat frequency increases on loading, then 
DOPPLER EFFECT
When a source of sound and an observer or both are in motion relative to each other there is an apparent change in frequency of sound as heard by the observer. This phenomenon is called the Doppler's effect.
Apparent change in frequency
- When source is in motion and observer at rest
- when source moving towards observer
- when source moving away from observer
Here V = velocity of sound
VS = velocity of source
ν0 = source frequency.
- When source is at rest and observer in motion
- when observer moving towards source
- when observer moving away from source and
V0 = velocity of observer.
- When source and observer both are in motion
- If source and observer both move away from each other.
- If source and observer both move towards each other.
- When the wind blows in the direction of sound, then in all above formulae V is replaced by (V + W) where W is the velocity of wind. If the wind blows in the opposite direction to sound then V is replaced by (V – W).
KEEP IN MEMORY
- The motion of the listener causes change in number of waves received by the listener and this produces an apparent change in frequency.
- The motion of the source of sound causes change in wavelength of the sound waves, which produces apparent change in frequency.
- If a star goes away from the earth with velocity v, then the frequency of the light emitted from it changes from ν to ν'.
ν' = ν (1–v/c), where c is the velocity of light and 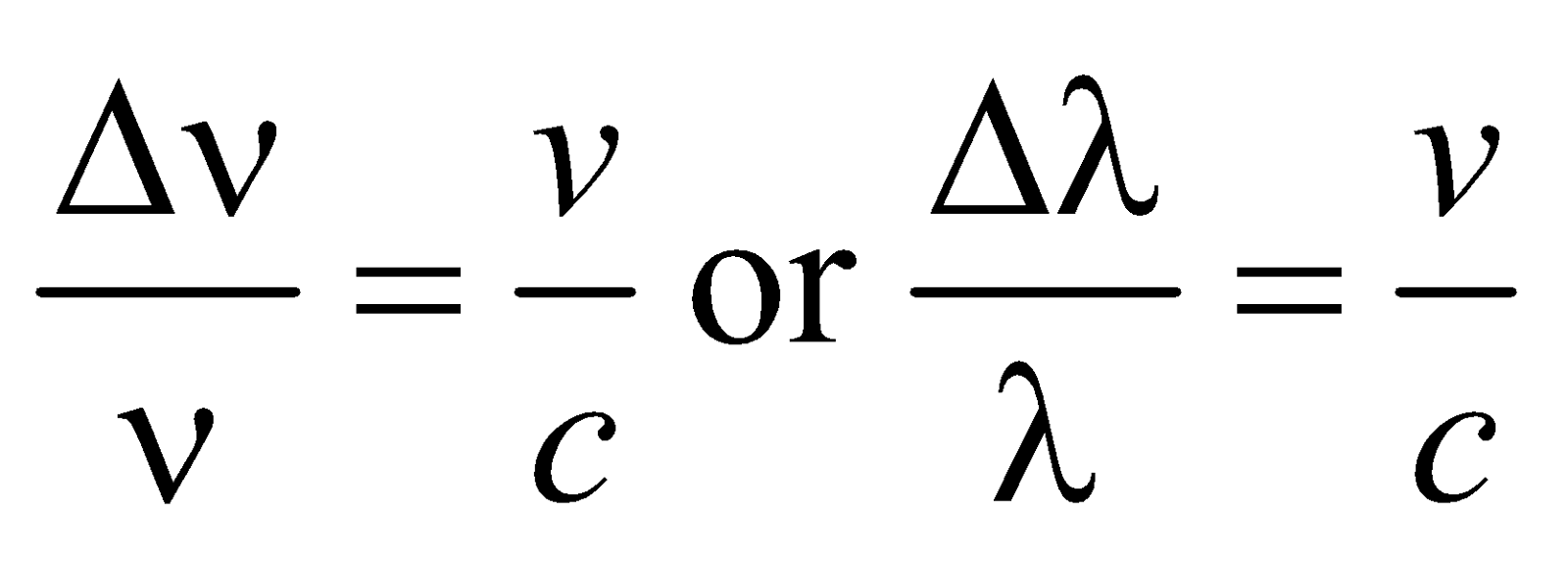 where
where  is called Doppler’s shift.
is called Doppler’s shift.
If wavelength of the observed waves decreases then the object from which the waves are coming is moving towards the listener and vice versa.
If wavelength of the observed waves decreases then the object from which the waves are coming is moving towards the listener and vice versa.
STATIONARY OR STANDING WAVES
When two progressive waves having the same amplitude, velocity and time period but travelling in opposite directions superimpose, then stationary wave is produced.
Let two waves of same amplitude and frequency travel in opposite direction at same speed, then
y1 = A sin (ωt –kx) and y2 = A sin (ωt + kx)
By principle of superposition
y = y1 + y2 = (2A cos kx) sin ωt ...(i)
y = AS sinωt
It is clear that amplitude of stationary wave As vary with position
- As = 0, when cos kx = 0 i.e., kx = π/2, 3π/2............
i.e., x = λ/4, 3λ/4...................[as k = 2π/λ]
These points are called nodes and spacing between two nodes is λ/2.
- As is maximum, when cos kx is max
i.e., kx = 0, π , 2π, 3π i.e., x = 0, λl/2, 2λ/2....
It is clear that antinode (where As is maximum) are also equally spaced with spacing λ/2.
- The distance between node and antinode is λ/4 (see figure)
KEEP IN MEMORY
- When a string vibrates in one segment, the sound produced is called fundamental note. The string is said to vibrate in fundamental mode.
- The fundamental note is called first harmonic, and is given by
, where v = speed of wave.
- If the fundamental frequency be
then
,
,
... are respectively called second third, fourth ... harmonics respectively.
- If an instrument produces notes of frequencies
.... where
....., then
is called first overtone,
is called second overtone,
is called third overtone ... so on.
- Harmonics are the integral multiples of the fundamental frequency. If ν0 be the fundamental frequency, then nν0 is the frequency of nth harmonic.
- Overtones are the notes of frequency higher than the fundamental frequency actually produced by the instrument.
- In the strings all harmonics are produced.
STATIONARY WAVES IN AN ORGAN PIPE
In the open organ pipe all the harmonics are produced.
In an open organ pipe, the fundamental frequency or first harmonic is , where v is velocity of sound and l is the length of air column [see fig. (a)]
(a) 
(b) 
(c) 
Similarly the frequency of second harmonic or first overtone is [see fig (b)], 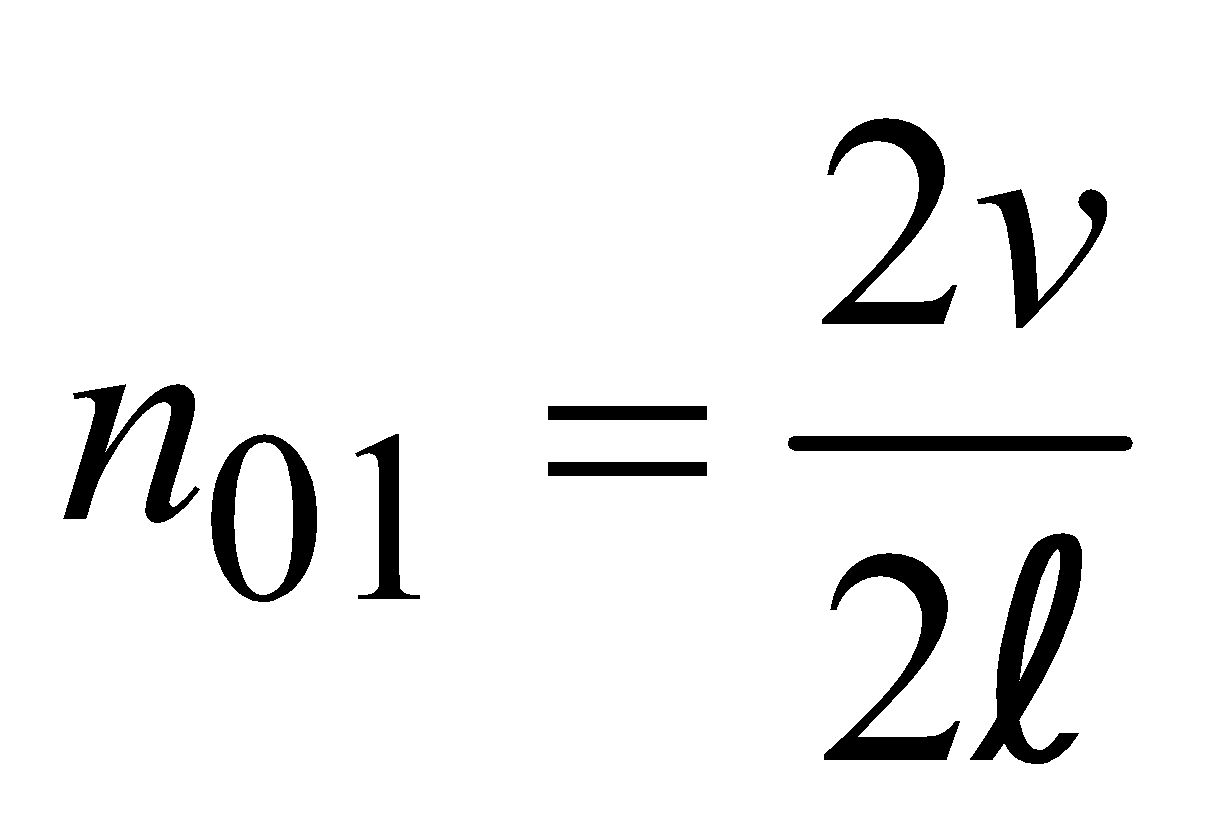
Similarly the frequency of third harmonic and second overtone is [(see fig. (c)] 
Similarly  ....
....
In the closed organ pipe only the odd harmonics are produced. In a closed organ pipe, the fundamental frequency (or first harmonic) is (see fig. a)
(a) 
 (b)
(b) 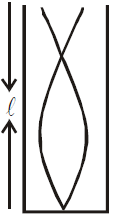
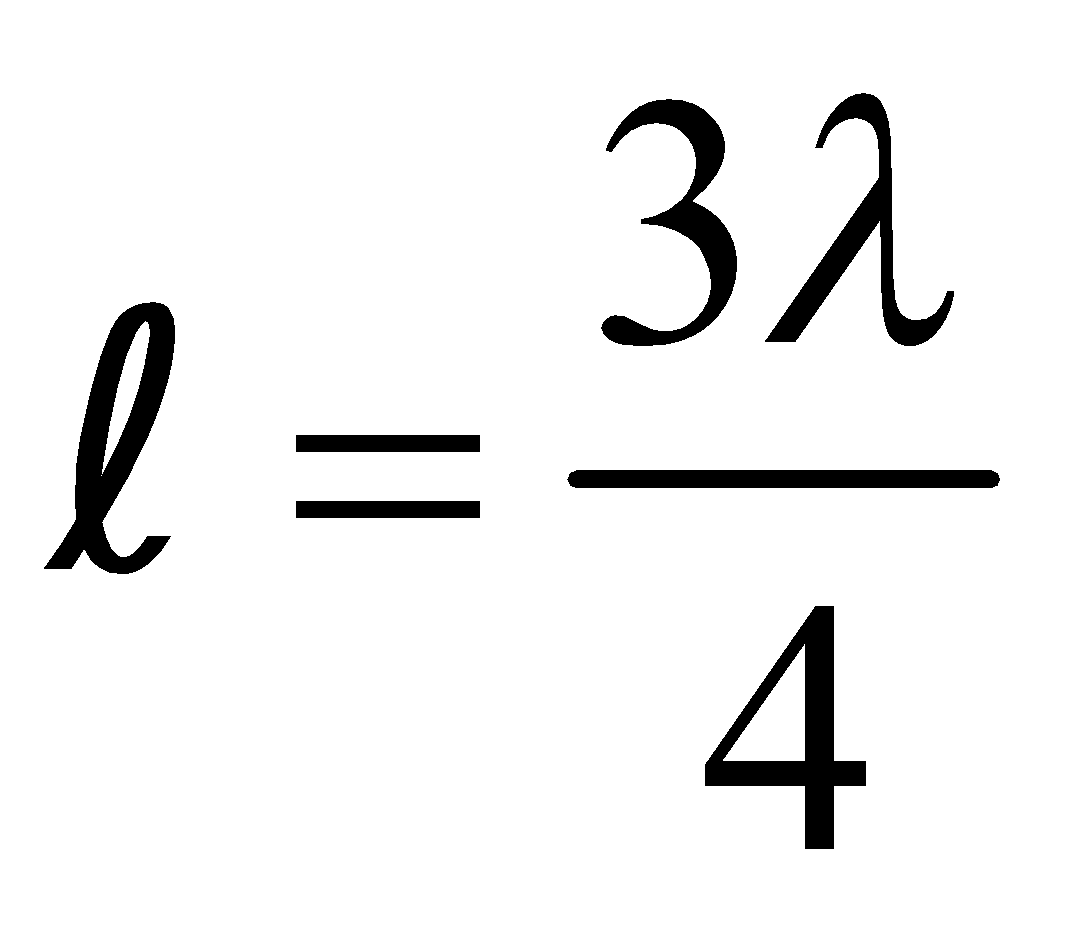 (c)
(c) 

Similarly the frequency of third harmonic or first overtone (IInd harmonic absent) is (see fig. b)
Similarly  ........
........
End Correction
It is observed that the antinode actually occurs a little above the open end. A correction is applied for this which is known as end correction and is denoted by e.
- For closed organ pipe : l is replaced by l + e where e = 0.3D, D is the diameter of the tube.
- For open organ pipe : l is replaced by l + 2e where e = 0.3D
In resonance tube, the velocity of sound in air given by v = 2v (l2-l1)
where ν = frequency of tuning fork, ll = 1st resonating length, l2 = 2nd resonating length.
RESONANCE TUBE
It is used to determine velocity of sound in air with the help of a tuning fork of known frequency.
Let l1 and l2 are lengths of first and second resonances then
Speed of sound in air is
For vibrating strings/open organ pipe
For closed organ pipe
COMPARISON OF PROGRESSIVE (OR TRAVELLING) AND STATIONARY (OR STANDING) WAVE
COMPARATIVE STUDY OF INTERFERENCE, BEATS AND STATIONARY WAVE
CHARACTERISTICS OF SOUND
Musical sound - consists of quick, regular and periodic succession of compressions and rarefactions without a sudden change in amplitude.
Noise - consists of slow, irregular and a periodic succession of compressions and rarefactions that may have sudden changes in amplitude.
Pitch, loudness and quality are the characteristics of musical sound.
- Pitch depends on frequency
- loudness depends on intensity
- quality depends on the number and intensity of overtones
Interval - The ratio of the frequencies of the two notes is called the interval between them. For example interval between two notes of frequencies 512 Hz and 1024 Hz is 1 : 2 (or 1/2).
Two notes are said to be in unison if their frequencies are equal, i.e., if the interval between them is 1 : 1. Some other common intervals, found useful in producing musical sound are the following:
Octave (1 : 2), majortone (8 : 9), minortone (9 : 10) and semitone (15 : 16)
Major diatonic scale - It consists of eight notes. The consecutive notes have either of the following three intervals. They are 8 : 9 ; 9 : 10 and 15 : 16.
ACOUSTICS
The branch of physics that deals with the process of generation, reception and propagation of sound is called acoustics.
Acoustics may be studied under the following three subtitles.
- Electro acoustics. This branch deals with electrical sound production with music.
- Musical acoustics. This branch deals with the relationship of sound with music.
- Architectural acoustics. This branch deals with the design and construction of buildings.
REVERBERATION
Multiple reflections which are responsible for a series of waves falling on listener’s ears, giving the impression of a persistence or prolongation of the sound are called reverberations.
The time gap between the initial direct note and the reflected note upto the minimum audibility level is called reverberation time.
Sabine Reverberation Formula for Time
Sabine established that the standard period of reverberation viz., the time that the sound takes to fall in intensity by 60 decibels or to one millionth of its original intensity after it was stopped, is given by 
where V = volume of room, 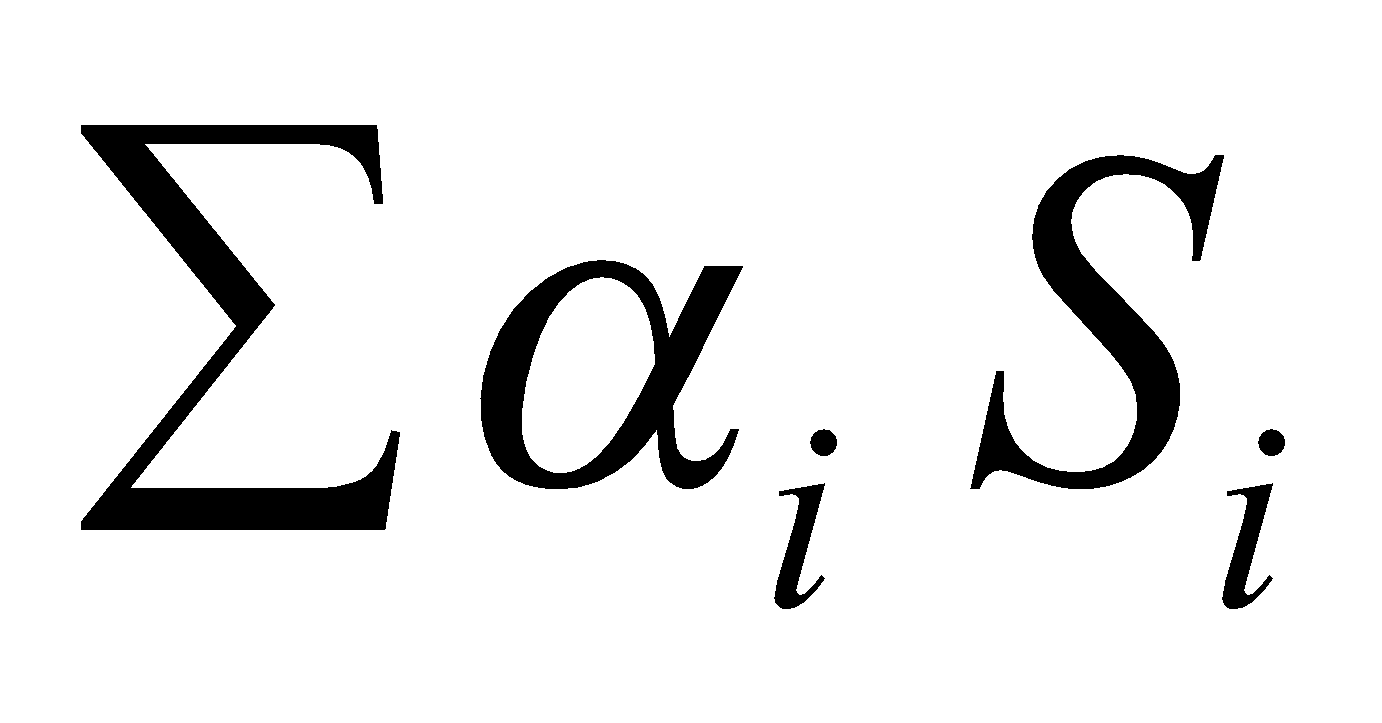 = α1 S1 + α2 S2 + ....
= α1 S1 + α2 S2 + ....
S1, S2 .... are different kinds of surfaces of room and
α1 , α2 .... are their respective absorption coefficient.
α1 , α2 .... are their respective absorption coefficient.
The above formula was derived by Prof C. Sabine.
SHOCK WAVES
The waves produced by a body moving with a speed greater than the speed of sound are called shock waves. These waves carry huge amount of energy. It is due to the shock wave that we have a sudden violent sound called sonic boom when a supersonic plane passes by.
The rate of speed of the source to that of the speed of sound is called mach number.
INTENSITY OF SOUND
The sound intensities that we can hear range from 10–12 Wm–2 to 103 Wm–2. The intensity level β, measured in terms of decibel (dB) is defined as 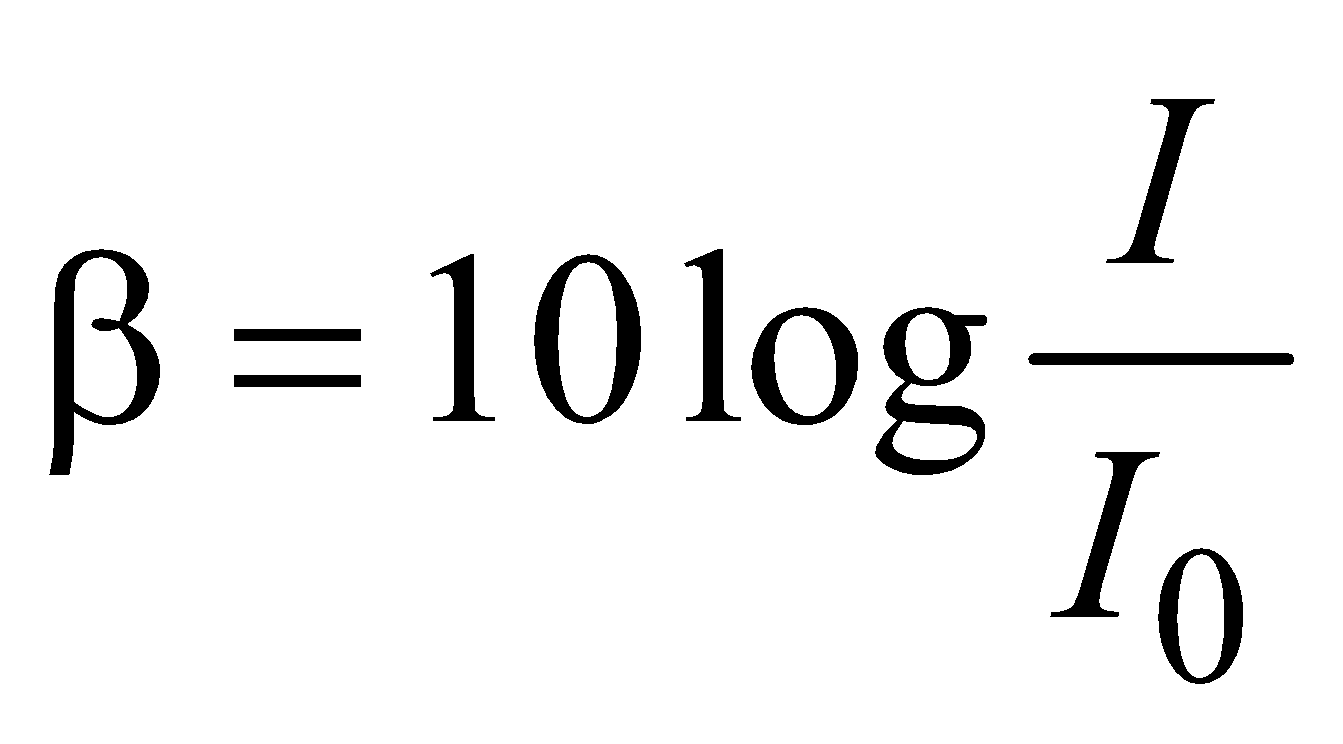
where I = measured intensity, I0 = 10–12 Wm–1
At the threshold β = 0
At the max 
LISSAJOUS FIGURES
When two simple harmonic waves having vibrations in mutually perpendicular directions superimpose on each other, then the resultant motion of the particle is along a closed path, called the Lissajous figures. These figures can be of many shapes depending on
- ratio of frequencies or time periods of two waves
- ratio of amplitude of two waves
- phase difference between two waves.



 9868233590
9868233590
